Description
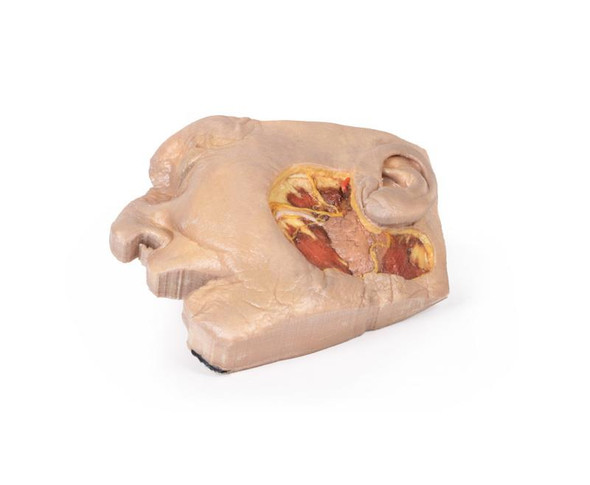
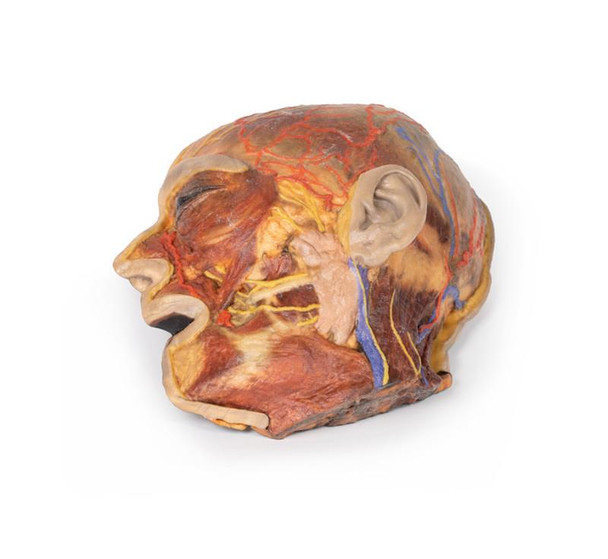
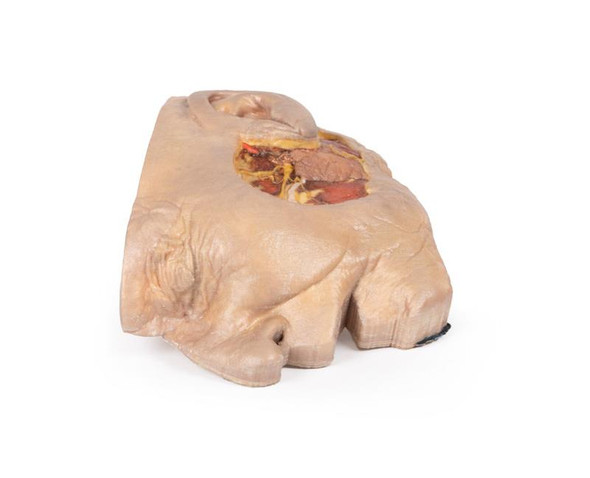
This 3D model presents the superficial anatomy of the face and head, and compliments the superficial facial anatomy of our HW 44 model with a more expanded dissection across the scalp and occipital regions.
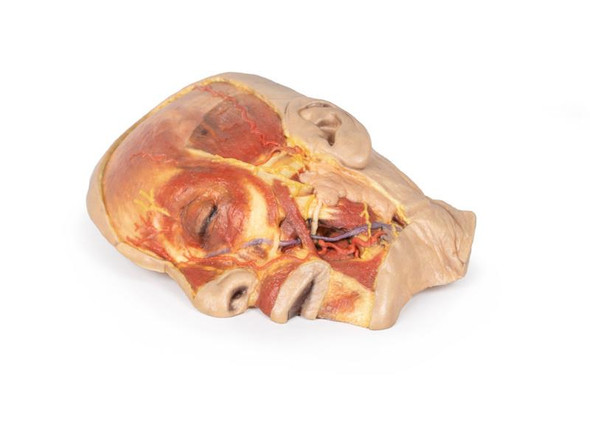
The superficial neurovascular and muscular structures in the face largely mirror the structures described in reference to our HW 44 specimen (see description), although the terminal branches of the facial nerve (CNVII) can be largely followed across a longer course from the parotid gland and the platysma muscle has been retained superficial to the mandible and extends towards the neck.
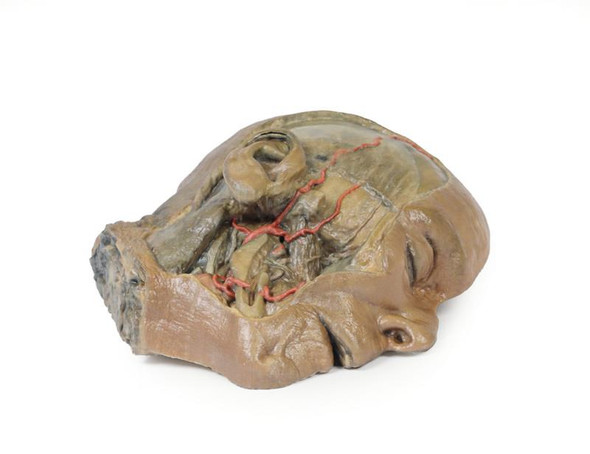
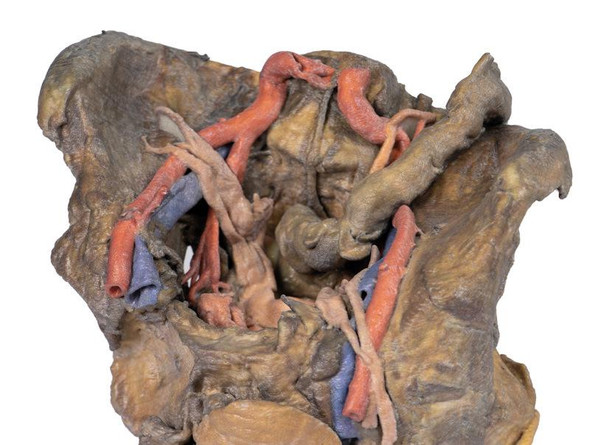
In contrast to the HW 44 specimen, this model has a more expansive superficial dissection inferior to the external ear and across the posterior scalp and occipital region. This allows for an expanded appreciation of the neurovascular distribution of the supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves and arties with the superficial temporal artery. Inferior to the ear, the retromandibular vein has been exposed with the ascending fibers of the great auricular nerve on its superficial surface (and further branches of this nerve on the surface of the sternocleidomastoid muscle). At the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle the lesser occipital nerve is just preserved, near the exiting and ascension of the occipital artery and vein near the trapezius muscle towards the posterior scalp. Surrounding the external ear are fibers of the auricularis superior and posterior muscles. Near the margin of the dissection window posteriorly the deep fibers of the occipitalis muscle can be seen integrated into the epicranius (occipitofrontalis) muscle.
Advantages
- Anatomically accurate and identical to real specimen
- No ethical issues - not real human body parts
- Reasonably priced
- Available within a short lead time
- Reproducible, several identical prints can be used as a classroom set
- Can be produced in different sizes to cater for the needs of the teacher
Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons
- Cadavers cost a lot money
- High cost for establishing your own plastination suite
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs
- Dissection of cadavers is a lot of staff time and that is a cost
- Storage of cadaver material needs special refrigeration etc. which has coast
- If you want another specimen you have to start all over again
Plastinates
- Costs
- Ethical issues
- Timeframe for plastination process
- Many countries do not allow their importation
- One of a kind
Superior 3D print results compared with conventional methods
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise and incredibly realistic
Clear Support Material
- To avoid breakage of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed on such spots. This makes the models robust and can be handled by students easily.